
With the continuous improvement of living standards, the public's attention to food safety has been increasing. In this context, traceability of fruits, especially green fruits, has become an objective requirement. Currently, pasting paper bar - code...
Contact Us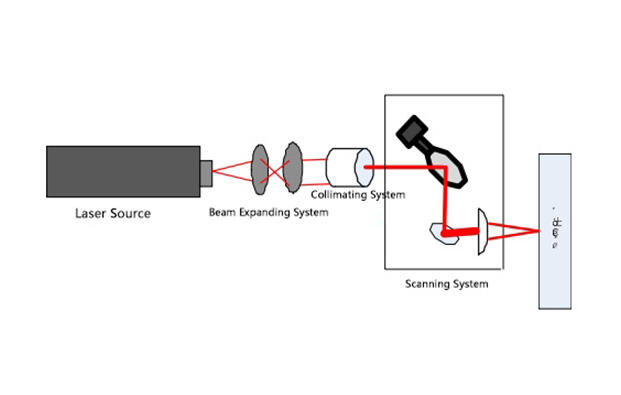
With the continuous improvement of living standards, the public's attention to food safety has been increasing. In this context, traceability of fruits, especially green fruits, has become an objective requirement. Currently, pasting paper bar - code labels on the surface of fruits is the main way to achieve fruit traceability. However, some paper labels are prone to falling off, resulting in the loss of key information, while others are so firmly attached that they are often difficult to remove. Therefore, this study selects oranges as the research object and intends to use laser technology to directly engrave two - dimensional barcodes on the fruit surface. By comparing the marking effects of ultra - short - pulse picosecond (ps) laser pulses and short - pulse nanosecond (ns) laser pulses, it aims to provide a marking technology with clear and durable barcodes for fruit traceability.
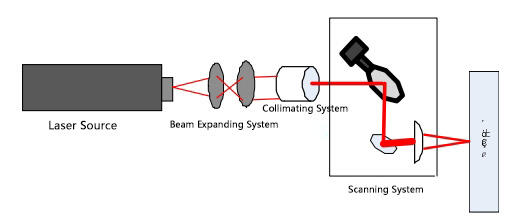
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of laser marking device


 EN
EN
 AR
AR CS
CS NL
NL FR
FR DE
DE IT
IT JA
JA KO
KO PL
PL PT
PT RU
RU ES
ES UK
UK TH
TH TR
TR